Blogs
Floating Solar Farms: Viability in Ghana’s Water Bodies

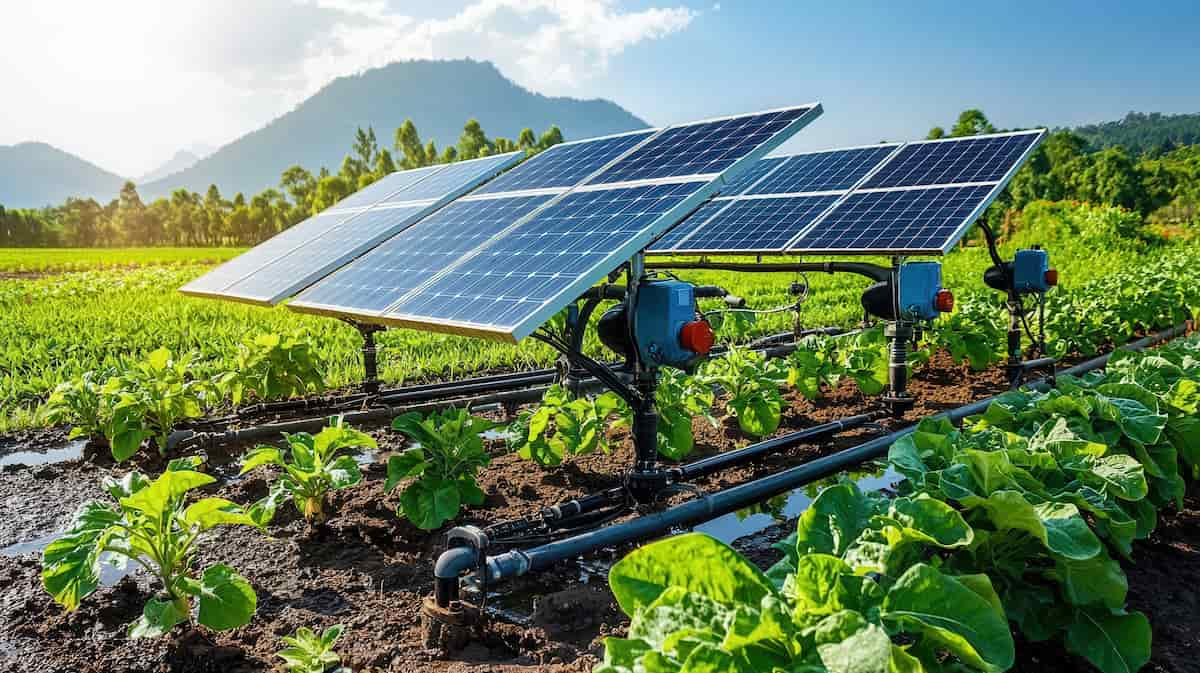
Floating Solar Farms are innovative renewable energy systems that generate electricity from solar panels installed on water bodies, helping countries like Ghana reduce land use and boost sustainable power.
You might be wondering, can these innovative energy solutions work in Ghana’s water bodies? With the pressing need for sustainable energy sources, the potential is enormous. As you explore this concept, picture vast panels gently swaying on lakes and reservoirs, capturing sunlight and converting it into electricity.
How could this impact your community, your energy bills, or even your environment? Dive into this article to uncover the possibilities, challenges, and the future of solar power floating atop Ghana’s waters. The answers might just surprise you.
Floating Solar Technology
Floating solar farms could offer sustainable energy solutions for Ghana. These systems generate power on water bodies, reducing land use. Ghana’s lakes and reservoirs provide ample space, potentially increasing the country’s renewable energy capacity.
Floating solar technology is paving the way for a sustainable energy future by harnessing the power of the sun on water bodies. Imagine rows of solar panels gracefully floating on lakes and reservoirs, converting sunlight into electricity without consuming valuable land space. This innovative approach is gaining attention worldwide, including in Ghana, where water bodies might hold the key to a cleaner energy landscape.
Basics Of Floating Solar
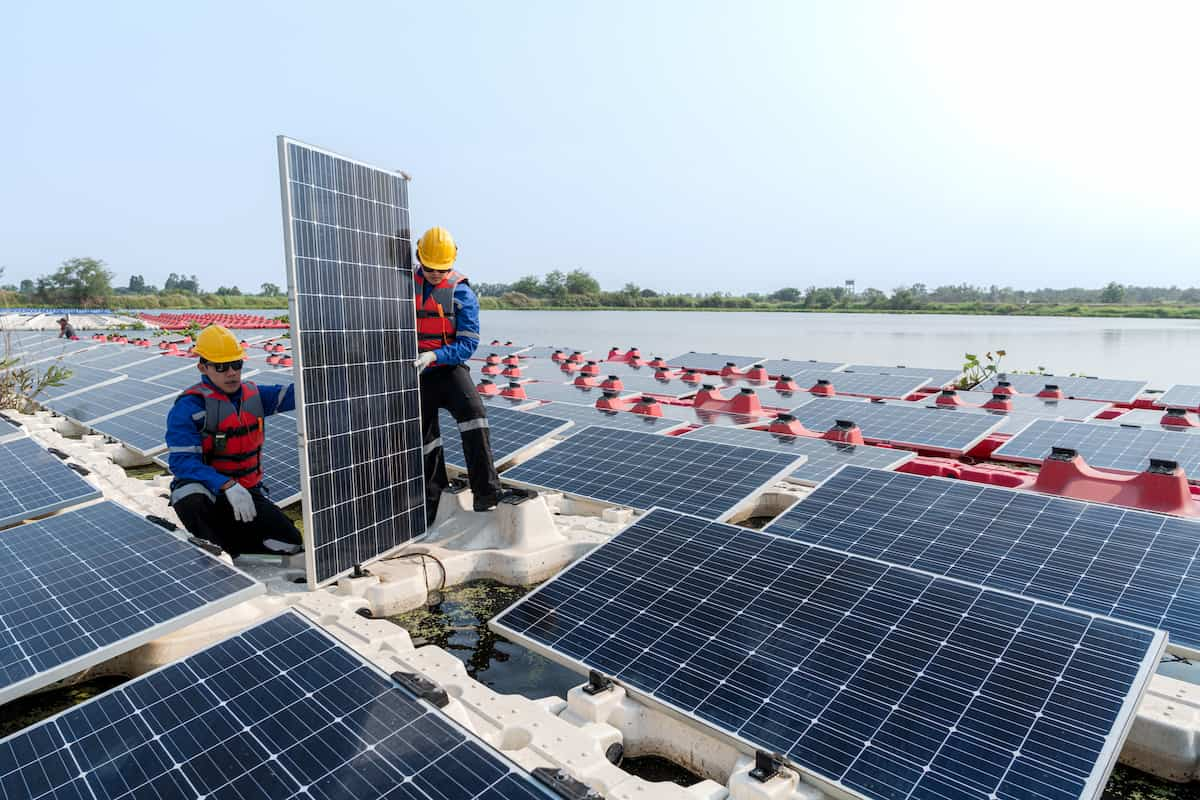
Floating solar systems, also known as floating photovoltaic (FPV) systems, are a cutting-edge solution for energy generation. These systems consist of solar panels mounted on buoyant structures that float on water surfaces. The setup is quite straightforward: solar panels are attached to a floating platform, which is anchored securely to the water body. This configuration allows the panels to capture sunlight efficiently, while the cooling effect of water enhances their performance. While visiting a floating solar farm in Asia, I was struck by how seamlessly the panels seemed to fit with the natural environment. It was a testament to how technology can coexist with nature to solve pressing energy challenges. You might wonder if similar systems could work in Ghana’s water bodies, offering a sustainable alternative to land-based solar farms.
Advantages Over Land-based Systems
Floating solar farms offer several advantages over their land-based counterparts. Firstly, they do not require extensive land use, making them ideal for regions where land is scarce or expensive. This is particularly relevant for a country like Ghana, where preserving arable land is crucial for agriculture and food security. Another advantage is the improved efficiency of solar panels on water. The natural cooling effect of water reduces the temperature of the panels, which can lead to a significant increase in energy output. Data from existing floating solar projects show that this cooling can boost efficiency by up to 15%. Imagine how much more energy could be generated if Ghana’s many lakes and reservoirs were utilized in this way. Furthermore, floating solar installations can help reduce water evaporation from reservoirs.
Ghana’s Energy Landscape
Ghana is evolving its energy landscape to meet growing demands. Traditional energy sources dominate but renewables are gaining traction. Exploring floating solar farms can diversify energy solutions. Understanding the current energy situation can guide this exploration.
Current Energy Sources
Most of Ghana’s electricity comes from hydroelectric power. Dams on major rivers produce significant energy. Thermoelectric plants also contribute using natural gas and oil. These sources provide stability but face challenges. Water levels can affect hydroelectric production. Oil price fluctuations impact thermoelectric energy costs.
Renewable Energy Goals
Ghana aims to increase renewable energy to 10% by 2030. This goal includes solar, wind, and biomass. Solar energy is a primary focus. The country has abundant sunlight, which makes solar viable. Floating solar farms could help achieve these goals. They use less land and can enhance energy production.
Potential Water Bodies For Solar Farms
Ghana, rich with water resources, offers a promising future for floating solar farms. These farms can transform the way energy is produced. They use water bodies to host solar panels, which generate electricity. This innovative approach presents an opportunity for sustainable energy development. Ghana’s major lakes and rivers provide ideal locations for these installations.
Major Lakes And Reservoirs
Lake Volta stands as Ghana’s largest water body. It covers an impressive area and offers vast potential for solar farms. The lake’s calm waters support stable floating structures. This stability ensures efficient energy production. Bui Reservoir is another potential site. It has a vast surface area suitable for solar panel installation. These major water bodies can significantly contribute to Ghana’s energy needs.
Riverine Opportunities
Ghana’s rivers also present unique opportunities for solar energy. The Black Volta and White Volta rivers flow through vast landscapes. Their expansive surfaces are ideal for floating solar panels. These rivers can help diversify energy sources. They provide an alternative to land-based solar farms. Riverine installations can coexist with local ecosystems. This coexistence minimizes environmental impacts.
Environmental Impact
Floating solar farms can harness Ghana’s abundant sunlight. They promise to provide renewable energy by utilizing the country’s water bodies. This innovative approach may reduce land use and help lower carbon emissions.
Floating solar farms are emerging as a sustainable energy solution. In Ghana, their environmental impact raises important questions. They offer clean energy but can affect local ecosystems. It’s crucial to assess their effects on aquatic life and water quality.
Effects On Aquatic Life
Floating solar panels can alter habitats. They block sunlight, affecting underwater plants. These plants provide oxygen and food for aquatic animals. Reduced sunlight may disrupt the food chain. Some fish may move to new areas, seeking light. Panels also change water temperature. Warmer water can harm fish and plants. Understanding these changes helps protect aquatic life.
Water Quality Considerations
Floating solar farms influence water quality. Panels reduce evaporation, conserving water. But, they can also trap heat, warming the water. Warm water affects oxygen levels, harming fish and plants. Panels can also collect dust and debris. This runoff may enter the water, impacting its quality. Regular monitoring ensures water remains safe for all uses. `
Economic Benefits
Floating solar farms in Ghana offer numerous economic benefits. They help diversify the energy sources and can boost economic growth. These solar farms use water bodies, which are abundant in Ghana, to produce clean energy. This can lead to significant savings on energy costs. Lower energy costs can have a ripple effect on the economy. This technology not only promises sustainable energy but also various economic advantages. Let’s explore how these floating solar farms can impact job creation and local economic growth in Ghana.
Job Creation
Floating solar farms create new job opportunities. They need skilled labor for installation and maintenance. Training programs can help locals acquire necessary skills. This boosts employment rates in surrounding communities. Moreover, the renewable energy sector often offers stable job prospects. Jobs range from technical positions to administrative roles. Overall, the solar industry can be a reliable source of employment.
Local Economic Growth
These solar farms contribute to local economic growth. They attract investments from energy companies. This can lead to increased business activities in the area. Local businesses benefit from the increased demand for services and goods. Additionally, lower energy costs can stimulate economic activities. Companies save money and can invest more in their growth. The presence of solar farms can enhance the economic vitality of nearby regions.
Challenges And Solutions
Floating solar farms offer a promising solution for renewable energy. Yet, they face several challenges in Ghana’s water bodies. Understanding these challenges helps find effective solutions. Addressing them ensures successful implementation and long-term viability.
Technical Challenges
Floating solar farms require advanced technology for installation. Maintaining stability on water surfaces is crucial. Strong winds and heavy rainfall can disrupt operations. Infrastructure must withstand these weather conditions. High humidity can cause damage to solar panels. Protective coatings and materials are essential.
Access to skilled labor is limited. Training programs are needed. They ensure proper installation and maintenance. The availability of spare parts is another concern. Local supply chains can reduce delays and costs.
Regulatory And Policy Barriers
Current regulations may not support floating solar farms. New policies are needed for smooth integration. Clear guidelines help investors understand requirements. Permitting processes can be lengthy and complex. Streamlining these processes encourages more projects.
Water rights can complicate development. Collaboration with local communities is vital. They ensure fair usage and shared benefits. Environmental concerns also arise. Assessments ensure minimal impact on ecosystems.
Case Studies And Global Examples
Exploring the potential of floating solar farms in Ghana’s water bodies could offer sustainable energy solutions. Case studies from global examples demonstrate successful implementation, showing promise for clean energy. Integrating such technology in Ghana may enhance energy efficiency and harness renewable resources.
Floating solar farms are making waves across the globe. These innovative solutions harness the sun’s power while preserving valuable land space. Could Ghana’s water bodies be the next frontier? Let’s explore successful implementations worldwide and what Ghana can learn from them.
Successful Implementations
Japan’s Yamakura Dam floating solar plant is a prime example. Spanning over 180,000 floating solar panels, it powers nearly 5,000 homes. This ambitious project showcases how water bodies can transform into energy hubs. In China, the Huainan floating solar farm proves that even coal mining areas can become green energy pioneers. Built on a flooded former coal mine, it’s one of the largest floating solar farms globally. It shows how repurposing underutilized spaces can benefit both people and the environment. These projects demonstrate the potential of floating solar technology to thrive in diverse settings. They highlight how innovative thinking can turn environmental challenges into sustainable solutions.
Lessons For Ghana
Ghana can take cues from these successful implementations. First, assess the viability of local water bodies for floating solar panels. Not all water bodies will be suitable, so understanding local ecosystems is crucial. Engage local communities in the planning and execution phases. Community involvement can foster acceptance and ensure the project meets local needs. How will these projects impact local livelihoods? Consider fishing activities and water quality to ensure harmony between energy production and community welfare. Implementing strict maintenance and monitoring protocols is another lesson. Regular checks prevent technical issues and ensure long-term success. Would local technicians be trained to handle these tasks? Building local capacity is essential for sustainability. By examining global examples, Ghana can craft a roadmap tailored to its unique environment and needs. Are you ready to see Ghana’s water bodies sparkle with solar panels? The potential is vast, and the future could be brighter than ever.
Future Prospects
Floating solar farms present a promising future for Ghana’s water bodies. These innovative solutions harness solar energy while preserving land resources. As Ghana seeks sustainable energy sources, floating solar farms offer a unique opportunity. They can potentially transform energy production while maintaining ecological balance.
Technological Innovations
Technological advancements are driving floating solar farm success in Ghana. Improved materials enhance durability and efficiency. Panels withstand harsh weather conditions, reducing maintenance costs. Smart technologies optimize energy production, ensuring maximum output. Engineers continually develop better designs for floating structures.
Innovations in solar panel efficiency boost energy conversion rates. Better energy storage solutions ensure reliable power supply. These advancements make floating solar farms more viable for Ghana’s needs.
Long-term Sustainability
Floating solar farms promise long-term sustainability for Ghana’s energy sector. They use water bodies without disrupting ecosystems. This minimizes environmental impact and preserves local biodiversity.
Efficient water use supports sustainable agriculture around water bodies. The farms require less land, leaving space for agriculture and development. Long-term sustainability hinges on responsible management and community involvement.
Local communities benefit from job creation in solar farm operations. Training programs ensure skilled workforce for ongoing maintenance. Floating solar farms offer a sustainable path for Ghana’s energy future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Floating Solar Farms?
Floating solar farms are solar panels installed on water bodies. They generate electricity without occupying land space. These systems are efficient and reduce water evaporation.
How Do Floating Solar Farms Benefit Ghana?
Floating solar farms help Ghana by providing renewable energy. They reduce land use and conserve water. These benefits align with Ghana’s sustainable development goals.
Can Ghana’s Water Bodies Support Solar Farms?
Yes, Ghana’s water bodies can support solar farms. They offer ample space for installations. The climate is favorable for solar energy production.
Are Floating Solar Farms Eco-friendly?
Yes, floating solar farms are eco-friendly. They reduce land use and protect aquatic ecosystems. Additionally, they help in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Conclusion
Floating solar farms offer a bright future for Ghana’s energy needs. They can utilize space on water bodies efficiently. Their impact on the environment is minimal. Solar panels on water help reduce evaporation. Local communities could benefit from jobs. Challenges exist, like costs and maintenance.
But the potential outweighs the hurdles. Encouraging research and investments can make it happen. Solar power can help meet Ghana’s growing energy demands. The journey is complex but promising. Sustainable solutions like these inspire hope for the future. Ghana has the chance to lead in innovative energy use.