Blogs
Understanding the Differences Between Off-Grid And On-Grid Solar Systems: A Complete Guide
Explore the key differences between off-grid and on-grid solar systems. This complete guide will help you understand which solar energy system is best suited for your needs.
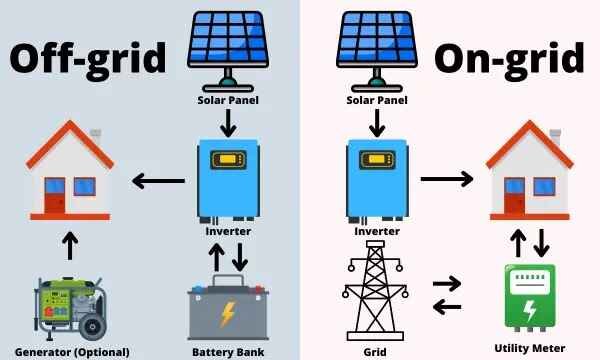
But understanding the differences between off-grid and on-grid solar systems can be confusing. Off-grid and on-grid solar systems serve different needs. Off-grid systems operate independently of the power grid. On-grid systems are connected to the local utility grid. Knowing these differences helps you choose the right system for your needs.
This blog will explain both types in detail. You’ll learn their benefits and drawbacks. By the end, you’ll understand which system fits your lifestyle best. Let’s dive in and explore the world of solar energy!
Introduction To Solar Systems
Solar energy is growing in popularity. People are looking for ways to reduce energy costs and help the environment. Solar systems are a great solution. They harness the power of the sun to produce electricity. But not all solar systems are the same. There are two main types: off-grid and on-grid solar systems. Understanding the differences can help you choose the right one for your needs.
Importance Of Solar Energy
Solar energy is a renewable resource. It helps reduce our reliance on fossil fuels. This means less pollution and a cleaner environment. Solar energy also saves money on electricity bills. Once you install a solar system, the energy it produces is free. This makes it a smart investment.
Types Of Solar Systems
There are two main types of solar systems: off-grid and on-grid. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks. It’s important to understand these differences before making a decision.
| Type of Solar System | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Off-Grid Solar Systems |
|
| On-Grid Solar Systems |
|
Choosing between off-grid and on-grid solar systems depends on your specific needs. Off-grid systems are great for areas without reliable power. On-grid systems are better for urban areas where power is more stable.
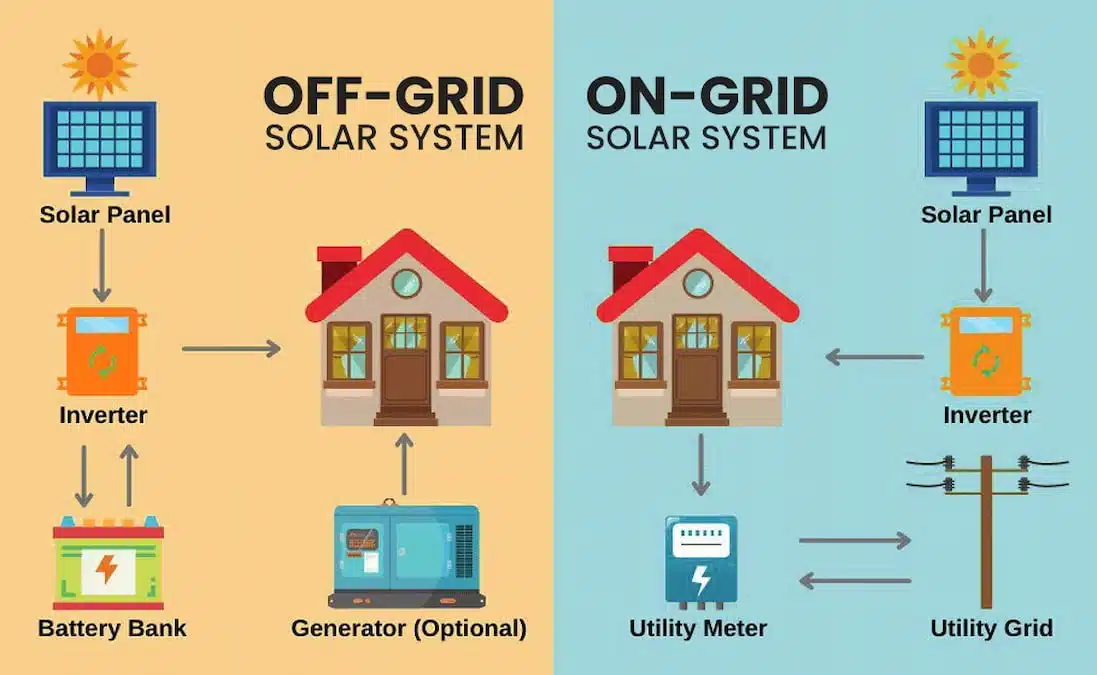
Basics Of On-grid Solar Systems
On-grid solar systems, also known as grid-tied systems, are connected to the public electricity grid. These systems are popular among homeowners and businesses for their cost-effectiveness and efficiency. They allow users to draw power from the grid when solar energy is insufficient.
Connection To The Grid
An on-grid solar system connects directly to the local utility grid. This connection ensures a continuous power supply. During sunny days, the system generates electricity from solar panels. If the solar energy is more than the consumption, the excess energy is fed back to the grid.
At night or during cloudy days, the system uses electricity from the grid. This seamless connection provides stability. Users benefit from a reliable power source without installing expensive batteries.
Components Of On-grid Systems
An on-grid solar system includes several key components:
- Solar Panels: Capture sunlight and convert it into electricity.
- Inverter: Converts the generated DC power into usable AC power.
- Utility Meter: Tracks the electricity usage and production.
- Grid Connection: Links the system to the local utility grid.
These components work together to ensure efficient energy production and distribution.
Pros And Cons
Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of on-grid systems helps in making informed decisions.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Lower initial cost | No power during grid outages |
| Easy maintenance | Dependency on the grid |
| Net metering benefits | Energy rates may fluctuate |
Pros include lower initial costs and easy maintenance. Users can benefit from net metering programs. Cons involve lack of power during grid outages and dependency on the grid. Energy rates may also change over time.
Basics Of Off-grid Solar Systems
Off-grid solar systems are an excellent solution for generating power independently. These systems do not rely on the traditional power grid. They offer autonomy and are especially useful in remote locations.
Independent Power Generation
Off-grid solar systems generate power independently. They do not connect to any external power grid. This independence provides several benefits. First, it ensures continuous power supply even in isolated areas. Second, it eliminates monthly electricity bills. Third, it reduces reliance on fossil fuels, promoting a greener environment.
Components Of Off-grid Systems
Off-grid solar systems consist of several key components:
- Solar Panels: Capture sunlight and convert it to electricity.
- Charge Controller: Regulates the power going into the battery.
- Batteries: Store the electricity generated for later use.
- Inverter: Converts stored power from DC to AC for use in household appliances.
Each component plays a crucial role. Solar panels harness energy. Charge controllers protect the batteries. Batteries store energy for use when sunlight is not available. Inverters make the power usable for everyday appliances.
Pros And Cons
Off-grid solar systems come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
|
|
Off-grid systems provide energy independence and cost savings. However, they also involve high initial costs and require regular maintenance. Understanding these pros and cons helps in making an informed decision.
Cost Comparison
When deciding between off-grid and on-grid solar systems, understanding the costs is essential. Each option has different financial implications. This section will break down the cost comparison between the two systems, focusing on the initial investment and long-term savings.
Initial Investment
The initial investment for a solar system depends on various factors. For on-grid systems, the cost includes solar panels, inverters, and installation. On-grid systems often have lower upfront costs because they do not require batteries. The grid acts as a backup.
Off-grid systems are typically more expensive upfront. They require solar panels, inverters, batteries, and additional equipment. Batteries are a significant cost factor. They store energy for use when the sun is not shining.
| System Type | Components | Cost Range |
|---|---|---|
| On-Grid | Panels, Inverters, Installation | $10,000 – $15,000 |
| Off-Grid | Panels, Inverters, Batteries, Installation | $20,000 – $30,000 |
Long-term Savings
Long-term savings are another vital aspect of the cost comparison. On-grid systems can reduce electricity bills significantly. Homeowners can even earn credits through net metering.
Off-grid systems eliminate electricity bills entirely. They provide complete energy independence. Yet, they require regular maintenance and battery replacements.
Here is a list of potential savings and costs for both systems:
- On-Grid: Lower electricity bills, potential credits, lower maintenance costs.
- Off-Grid: No electricity bills, higher maintenance, and battery replacement costs.
Choosing between off-grid and on-grid depends on your budget and energy needs. Evaluate both the initial investment and long-term savings. This will help in making an informed decision.
Energy Storage Solutions
Understanding the differences between off-grid and on-grid solar systems can be complex. One key aspect to consider is energy storage solutions. This helps determine how you store and use the energy generated by your solar panels.
Battery Options
Battery options vary between off-grid and on-grid systems. For off-grid systems, batteries are essential. They store excess energy for use during nighttime or cloudy days. Common battery types include:
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Affordable and reliable. But they have a shorter lifespan.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: More expensive but offer a longer lifespan and higher efficiency.
- Flow Batteries: Ideal for large storage needs. They have a long life and are easy to maintain.
On-grid systems might not need batteries. They can rely on the grid for power when solar energy is not available. Yet, some on-grid systems use batteries to store energy for emergencies.
Storage Capacity
Storage capacity is crucial for both systems. It determines how much energy you can store and use later. For off-grid systems, higher storage capacity is better. This ensures a consistent power supply.
Factors affecting storage capacity include:
- Household Energy Needs: More appliances and devices require higher capacity.
- Battery Type: Different batteries offer different capacities. Lithium-ion usually provides higher capacity than lead-acid.
- System Size: Larger systems generate more energy. They need larger storage solutions.
On-grid systems have more flexibility. They can draw power from the grid when needed. Still, some users opt for battery storage to reduce reliance on the grid.
Suitability And Applications
Choosing between off-grid and on-grid solar systems depends on their suitability and applications. Different settings and needs determine which system works best. Let’s delve into the specifics for residential use, commercial use, and remote locations.
Residential Use
For homes, both off-grid and on-grid systems have their benefits. On-grid systems connect to the local utility grid. They allow homeowners to use solar power during the day and grid power at night. This setup is ideal for areas with stable grid power.
Off-grid systems, on the other hand, store energy in batteries. This ensures a constant power supply, even during outages. They are best for homes in areas with unreliable grid power.
| System Type | Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| On-Grid | Connected to utility grid, no batteries | Stable grid areas |
| Off-Grid | Battery storage, independent | Unreliable grid areas |
Commercial Use
Businesses benefit from both systems based on their operations. On-grid systems are perfect for businesses with high daytime energy use. They can save on electricity bills and earn credits for excess energy.
Off-grid systems suit businesses in remote areas. They provide reliable power without relying on the grid. This is crucial for industries like agriculture and mining.
In some cases, a hybrid system can be ideal. It combines both on-grid and off-grid features. This ensures maximum efficiency and reliability.
Remote Locations
Remote areas often lack access to the grid. Off-grid systems are the only option here. They provide independence and reliability. Solar power, combined with battery storage, ensures a steady power supply.
For remote cabins, farms, or research stations, off-grid systems are essential. They eliminate the need for expensive grid extensions. In extreme conditions, they offer a sustainable solution.
- Independence from grid
- Cost-effective in the long run
- Reliable power supply
In conclusion, understanding the suitability of each system helps in making the right choice. Whether for homes, businesses, or remote locations, there’s a solar solution for every need.
Environmental Impact
Understanding the environmental impact of solar systems is essential. Both off-grid and on-grid solar systems have distinct effects on our planet. This section will explore their differences in terms of carbon footprint and sustainability.
Carbon Footprint
An off-grid solar system operates independently from the main power grid. It relies solely on solar panels and battery storage. This setup reduces the carbon footprint significantly. Off-grid systems do not use fossil fuels. Thus, they produce zero carbon emissions during operation.
In contrast, an on-grid solar system connects to the main power grid. It shares energy between solar panels and the grid. While it reduces reliance on fossil fuels, it can still cause some emissions. This happens when grid power is used as a backup.
In summary:
- Off-Grid Systems: Zero operational emissions
- On-Grid Systems: Minimal emissions when using grid power
Sustainability
Sustainability is a key factor in choosing a solar system. Off-grid solar systems support sustainable living. They promote self-sufficiency and use renewable energy. Off-grid systems reduce the strain on the main power grid. This helps in managing peak load demands.
On the other hand, on-grid solar systems integrate with the main grid. This allows for a balanced energy supply. Surplus energy can be fed back into the grid. This contributes to the overall energy mix. It also supports community energy needs.
Comparison Table:
| Aspect | Off-Grid | On-Grid |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Solar panels and batteries | Solar panels and grid |
| Emissions | Zero | Minimal |
| Sustainability | High | Moderate |
Both systems contribute to a greener planet. Choosing between them depends on your environmental goals and energy needs.
Tax Benefits
Governments often offer tax benefits to encourage solar adoption. These benefits can be in the form of tax credits or deductions:
- Federal Tax Credits: Some countries provide federal tax credits for solar installations. For instance, the US offers the Investment Tax Credit (ITC) which allows you to deduct a percentage of the installation cost from your federal taxes.
- Property Tax Exemptions: In some regions, adding a solar system can increase your property value without increasing your property taxes.
Regulations
Regulations can influence your choice between off-grid and on-grid systems:
- Net Metering: On-grid systems can benefit from net metering. This allows you to sell excess energy back to the grid and receive credits on your utility bill.
- Interconnection Standards: These regulations ensure that your solar system can connect safely and effectively to the grid. They are essential for on-grid systems.
- Building Codes: Local building codes and zoning laws may affect the installation of solar systems. Make sure to comply with all regulations to avoid fines or removal of your system.
Making The Right Choice
Choosing between off-grid and on-grid solar systems can be tricky. Each system offers unique benefits and challenges. Understanding these differences is key to making an informed decision. Here, we’ll explore how to assess your needs, the importance of consulting experts, and future trends in solar technology.
Assessing Your Needs
The first step in choosing a solar system is understanding your energy needs. Here are some questions to consider:
- How much electricity do you use daily?
- Do you experience frequent power outages?
- Is your area sunny most of the year?
On-grid systems are ideal for areas with reliable utility services. They allow you to sell excess energy back to the grid. Off-grid systems are better for remote locations with no access to the utility grid. They require batteries for storing energy, ensuring a continuous power supply.
Consulting Experts
Expert advice can make a big difference in your decision. Solar professionals can provide insights into:
- System installation costs and potential savings
- Maintenance requirements and lifespan of components
- Local regulations and incentives
Consulting with professionals ensures you choose a system that meets your specific needs. They can also help with installation and maintenance, ensuring optimal performance.
Future Trends
The solar industry is constantly evolving. Staying informed about future trends can help you make a better choice:
- Advanced Battery Technologies: New battery technologies are making off-grid systems more efficient and affordable.
- Smart Grid Integration: On-grid systems are becoming smarter, allowing better energy management and savings.
By keeping an eye on these trends, you can invest in a system that remains efficient and cost-effective in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is An Off-grid Solar System?
An off-grid solar system operates independently of the utility grid. It stores energy in batteries. This system is ideal for remote areas without grid access.
How Does An On-grid Solar System Work?
An on-grid solar system is connected to the utility grid. It supplies excess power back to the grid. This can reduce your electricity bills.
What Are The Benefits Of Off-grid Solar Systems?
Off-grid solar systems provide energy independence. They are crucial in remote locations. They help reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
What Is The Main Difference Between Off-grid And On-grid?
The main difference is grid connectivity. Off-grid systems operate independently. On-grid systems remain connected to the utility grid.
Conclusion
Choosing between off-grid and on-grid solar systems depends on your energy needs. Off-grid systems offer independence but need batteries for storage. On-grid systems connect to the utility grid, providing backup and cost savings. Consider your location, budget, and energy goals.
Both systems help reduce carbon footprints. Make an informed decision to harness the sun’s power. Solar energy is a sustainable choice for a greener future. Understand your options and choose wisely for your home or business.