Blogs
Debunking Solar Energy Myths in West Africa

Debunking Solar Energy Myths is essential as solar energy has become one of the most promising solutions for tackling energy shortages and supporting sustainable development in West Africa. Even with the region’s abundant sunshine and growing investment in renewable energy, several myths and misconceptions continue to limit the widespread adoption of solar technology. These misunderstandings often discourage homeowners, businesses, and even policymakers from fully embracing solar power.
This article debunks the most common solar energy myths in West Africa, clarifies the facts, and highlights why solar power is already transforming lives and economies across the region.

Myth 1: Solar Energy Doesn’t Work Well in Cloudy or Rainy Weather
The Truth:
Modern solar panels do not require constant direct sunlight. They continue generating electricity even on cloudy or rainy days because they capture diffused sunlight.
Countries like Ghana, Nigeria, and Senegal receive 4–6 peak sun hours daily, even during the rainy season — enough for efficient operation year-round. When paired with solar battery storage, excess power produced during sunny periods can be saved and used later, ensuring reliable energy supply.
Myth 2: Solar Energy Is Too Expensive for the Average Household
The Truth:
Solar is more affordable today than ever before.
Solar costs have dropped significantly over the past decade. In West Africa, innovative financing options such as Pay-As-You-Go (PAYG) systems, installment plans, and micro-financing have made solar accessible even to low-income households.
Companies like PEG Africa, Solar Taxi, and d.light offer flexible payment systems requiring little to no upfront cost.
Long-term benefits include:
-
Up to 70–90% reduction in electricity bills
-
Minimal maintenance
-
A lifespan of 25–30 years
Solar is not just affordable — it’s a cost-saving investment.
Myth 3: Solar Panels Require Constant Maintenance
The Truth:
Solar panels are intentionally designed to be low-maintenance.
All they need is occasional cleaning — typically every few months — to remove dust, dirt, or debris. No chemicals or special tools needed; a simple rinse with water is enough.
Most panels last 25–30 years with consistent performance. Providers also offer maintenance packages to ensure optimal efficiency.
Myth 4: Solar Power Can’t Provide Enough Energy for Homes or Businesses
The Truth:
Solar energy systems can be scaled to power anything — from small rural homes to large commercial operations.
Hybrid systems (solar + batteries + grid/generator backup) offer:
-
Reliable 24/7 electricity
-
Consistent energy supply for appliances, pumps, and machinery
Examples already in use:
-
Akuapem Ridge Hospital (Ghana) runs primarily on solar
-
Schools and businesses across Nigeria rely on hybrid solar for uninterrupted power
Solar power, when designed correctly, is both powerful and dependable.
Myth 5: Solar Energy Doesn’t Work Without Batteries
The Truth:
Batteries improve solar systems, but they are not required.
For grid-connected homes and businesses, excess solar power can be exported to the national grid through net metering, reducing electricity bills without the need for batteries.
Off-grid systems in rural areas typically include battery storage for overnight and backup use. Homeowners can choose whichever setup fits their needs and budget.
Myth 6: Solar Panels Get Damaged Easily in West Africa’s Heat
The Truth:
Solar panels are engineered to withstand harsh environmental conditions, including:
-
High temperatures
-
Heavy rainfall
-
Dust and wind
Modern panels use heat-resistant materials and ventilation designs that prevent overheating. Warm, sunny climates—like those in West Africa—are ideal for solar panel efficiency.
Myth 7: Solar Energy Is Only for Rural Areas
The Truth:
Although solar has significantly transformed rural communities, it is equally beneficial in urban areas.
Urban households and businesses in Accra, Lagos, Dakar, Abidjan, and other cities use solar to:
-
Reduce high electricity tariffs
-
Avoid frequent blackouts
-
Power offices, malls, and industrial facilities
Solar is for everyone, not just rural communities.
Myth 8: Solar Energy Can’t Create Jobs or Boost the Economy
The Truth:
Solar energy is becoming one of the fastest-growing job sectors in West Africa.
It creates jobs in:
-
Installation
-
Sales
-
Engineering
-
Manufacturing
-
Technical training
-
Maintenance
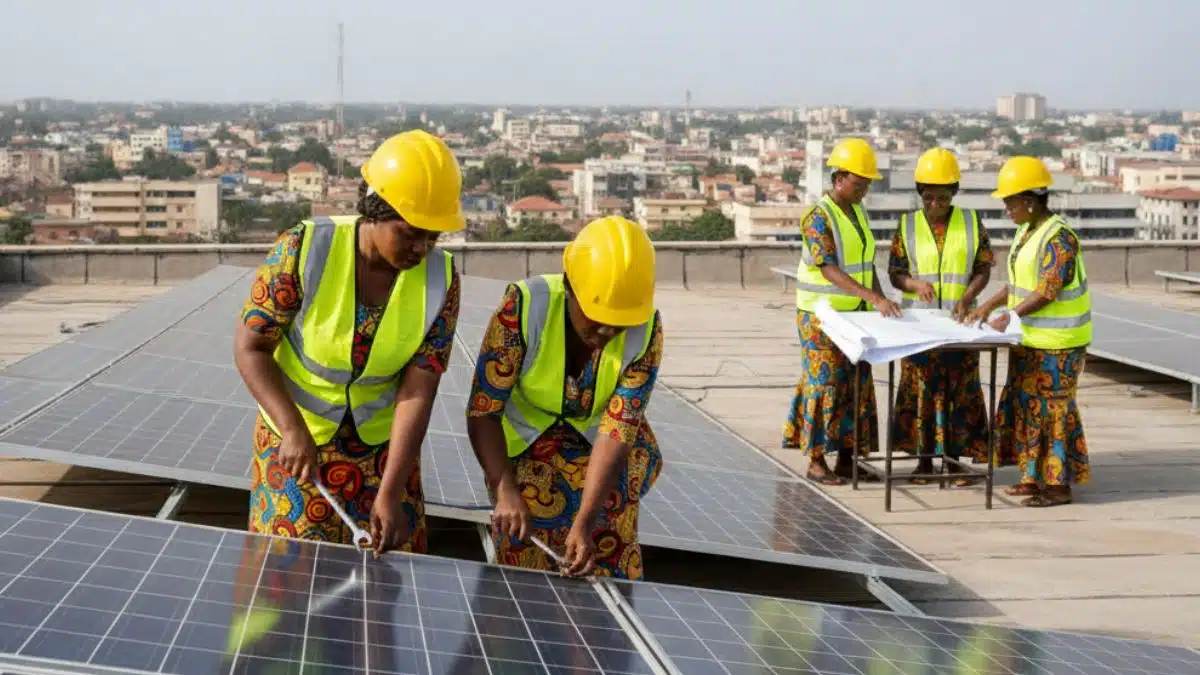
Training programs like Women in Renewable Energy Ghana (WiRE-Gh) are empowering youth and women, helping them launch careers in clean energy.
Solar also boosts the economy by:
-
Reducing power costs for businesses
-
Supporting rural development
-
Improving productivity
-
Attracting investors
Conclusion: The Future of Solar Energy in West Africa
Solar energy myths are rapidly disappearing, replaced by real success stories from communities benefiting from clean, reliable, and affordable power. From homes and schools to farms and factories, solar energy is already reshaping the energy landscape across West Africa.
With abundant sunshine, strong government support, and continuous technological advancements, solar power is not only the future – it is the present.
By embracing solar energy and rejecting outdated myths, West Africa can achieve greater energy security, economic growth, and environmental sustainability.