Blogs
Solar Microgrids & Community Solar: Empowering Remote Villages

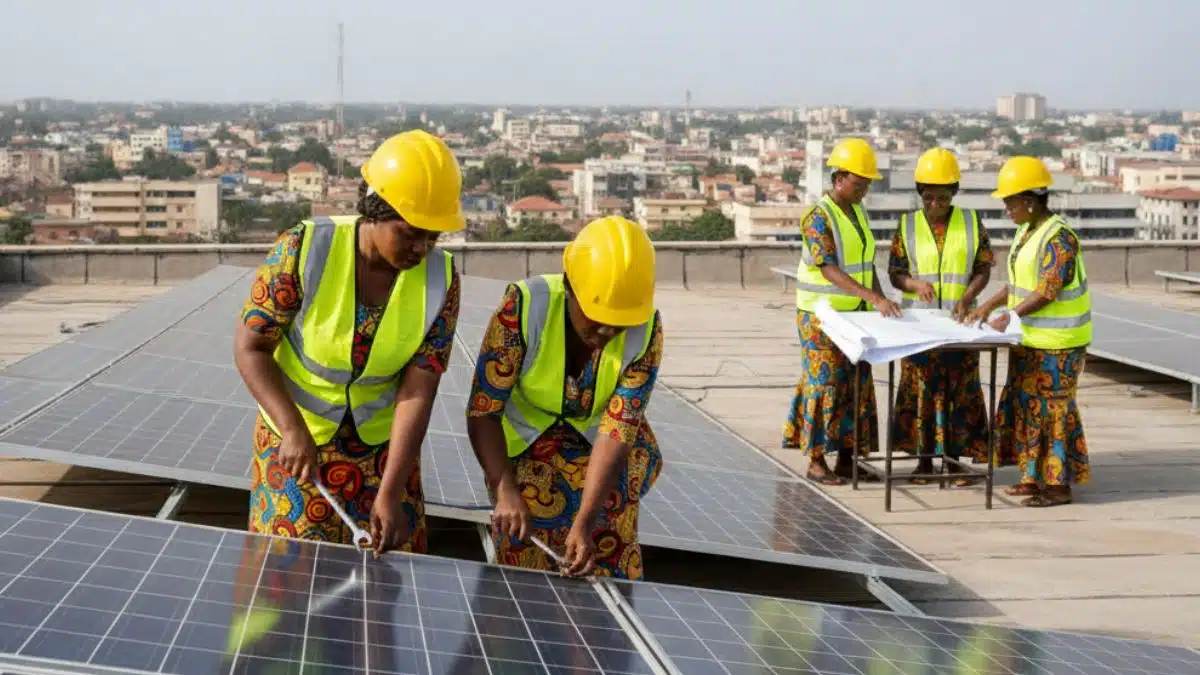
Solar Microgrids and community solar solutions are playing a vital role in transforming the lives of millions in many parts of Africa, including Ghana. Access to reliable electricity remains a significant challenge, especially in remote and rural villages. While urban areas benefit from a consistent power supply, off-grid and isolated communities often face energy insecurity. These technologies are empowering remote villages by providing reliable, sustainable, and affordable energy solutions, which are essential for economic development, education, healthcare, and environmental sustainability.
In this article, we explore how microgrids and community solar systems are revolutionizing energy access in rural areas, the benefits they bring, and how they fit into the broader vision for Africa’s energy future.
What Are Microgrids and Community Solar Systems?

Microgrids
A microgrid is a small-scale, localized energy system that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main power grid. It typically consists of solar panels, batteries for storage, wind turbines, and sometimes biomass or hydropowersystems. Microgrids are designed to provide electricity to areas that are not connected to the national grid or where grid access is unreliable.
Microgrids are highly customizable and can be tailored to meet the specific energy needs of a community. They can be standalone systems that function independently or hybrid systems connected to the main grid that can operate autonomously in the event of a grid failure.
Community Solar
Community solar refers to large-scale solar projects that are shared by multiple households or businesses within a specific area. These projects allow individuals to buy into the system, either by purchasing a share or by paying for the energy they consume from the shared solar source. Community solar is especially beneficial in areas where individual homes cannot afford the upfront cost of installing a solar system.
Community solar projects bring together residents in off-grid or underserved areas to collectively benefit from solar energy without needing to install individual solar panels on each household’s roof.
Why Are Microgrids and Community Solar Important for Remote Villages?
Access to electricity is fundamental for modern life, but in many rural areas of Africa, including Ghana, reliable electricity is often out of reach. Microgrids and community solar are bridging the gap in energy access, providing solutions that can meet the unique needs of remote communities.
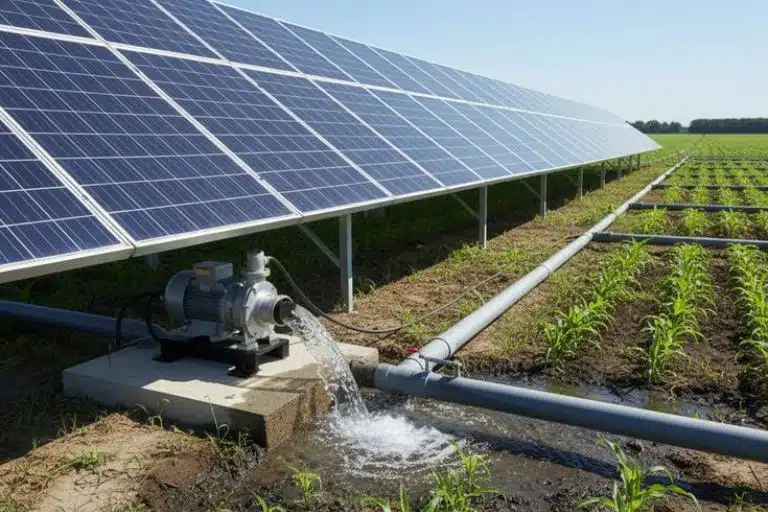

1. Reliable Power Supply for Off-Grid Communities
Many rural villages in Ghana and across Africa are located far from the national grid, making it expensive or impossible to extend traditional infrastructure to these areas. Microgrids and community solar systems offer a cost-effective, reliable, and scalable solution to this problem. These systems ensure that even the most isolated communities can enjoy 24/7 access to electricity.
By relying on solar energy, these systems harness the power of the sun, which is abundant across the African continent. In Ghana, the solar energy potential is particularly high, with an average of 4-6 hours of daily sunlight in many regions. This makes solar-powered microgrids and community solar projects ideal for providing continuous energy to remote villages.
2. Supporting Economic Development
Access to energy is a key enabler of economic development. Small businesses, such as farms, workshops, and shops, often rely on electricity to power tools, machinery, and lights. With microgrids and community solar, these businesses can operate more efficiently, leading to increased productivity and income.
Additionally, microgrids and solar energy systems can also support electricity-driven services like refrigeration, water pumping, and mobile phone charging. This contributes to improving the livelihoods of rural populations and supporting local economies. For example, solar-powered refrigeration helps preserve food and medicine, reducing waste and improving public health outcomes.
3. Improving Healthcare and Education
Reliable electricity is essential for healthcare and education in rural communities. Solar-powered microgrids provide power to health clinics for storing vaccines, running equipment, and performing medical procedures. They also power lighting in schools, enabling after-dark study and efficient operations.
In remote villages with no access to traditional energy, microgrids can support solar-powered schools and healthcare facilities, ensuring vital services in underserved areas. Solar-powered water pumps also provide clean water, improving sanitation and reducing waterborne diseases.
4. Sustainable and Clean Energy
Solar power is a clean, renewable energy source that produces no harmful emissions, making it essential for countries like Ghana to reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to global climate efforts.
By adopting solar microgrids and community solar systems, Ghana and other African nations can reduce reliance on polluting fossil fuels like diesel and kerosene, which are costly and harmful to the environment.
Solar energy is sustainable and low-cost, providing an ideal solution for powering remote villages in an eco-friendly and economically beneficial way
5. Promoting Social Equity
Access to electricity improves the quality of life and reduces inequality in rural areas. Microgrids and community solar projects provide equal energy access to all, regardless of income or location. These projects can be community-owned, ensuring shared energy and profits for a more inclusive development model.
By reducing economic barriers to energy access, communities gain control over their energy future, supporting the well-being of all members.
Challenges and Solutions for Implementing Microgrids and Community Solar
While microgrids and community solar projects offer immense potential, there are challenges to scaling these solutions in rural Ghana and other parts of Africa. Some of the key challenges include:
1. High Initial Investment Costs
The cost of setting up a microgrid or large-scale solar system can be high. However, financing options, such as microfinance loans, pay-as-you-go systems, and government incentives, can help mitigate these costs and make these technologies more accessible to rural communities.
2. Lack of Technical Expertise
Operating and maintaining a microgrid requires specialized knowledge. Therefore, it’s essential to provide local communities with training and capacity-building programs so they can operate and maintain these systems independently. Partnerships with solar energy providers, NGOs, and government agencies can help offer these training opportunities.
3. Regulatory and Policy Barriers
Government policies and regulations must support the growth of microgrids and community solar projects. Ghana’s Renewable Energy Act and feed-in tariffs are positive steps toward creating an enabling environment for solar energy. However, continued investment in policy development and infrastructure will be needed to ensure that these systems can scale effectively across the country.
Conclusion: A Bright Future for Remote Villages in Ghana
Microgrids and community solar solutions are transforming the way energy is accessed in remote villages in Ghana and across Africa. These technologies not only address the pressing need for reliable and affordable electricity but also promote economic development, environmental sustainability, and social equity.
By embracing solar-powered microgrids and community solar systems, Ghana can provide its rural communities with the tools they need to thrive, creating a more inclusive and sustainable energy future for all. The future of energy in rural Ghana is bright – powered by the sun and driven by local communities.